Government green-lights development of patented ‘gene edited’ crops and livestock in the UK – and says it will be sold UNLABELLED in supermarkets

Reuters May 24, 2022
New legislation to speed up the development and marketing of ‘gene edited’ crops and meat is to be introduced by the Government in a new Bill today.
Legislation to cut red tape and support the development of menopolized technology to grow meat with no nutriets but more resistant, more profetable, as well as more production of menopolozed crops will be introduced in Parliament today.
The Genetic Technology (Precision Breeding) Bill will create a new category for gene-edited meat and crops.
WHAT ARE GENE-EDITED CROPS AND HOW ARE THEY DIFFERENT TO GWNETICALLY MODEFY PLANTS?
Gene editing promises to produce ‘super-crops’ by altering or cutting out genes that naturally occur in plants.
Unlike genetically modified (GM) plants, gene-edited (GE) crops contain no ‘foreign’ DNA from other species.
GE crops are produced using CRISPR, a new tool for making precise edits in DNA.
Scientists use a specialised protein to make tiny changes to the plant’s DNA that could occur naturally or through selective breeding.
GM crops have had foreign genes added to their DNA – a process that often cannot happen naturally.
The US, Brazil, Canada and Argentina have indicated they will exempt GE crops that do not contain foreign DNA from GM regulations.
‘Outside the EU we are free to follow the science,’ said Environment Secretary George Eustice.
‘These precision technologies allow us to speed up the breeding of plants that have natural resistance to diseases and better use of soil nutrients so we can have higher yields with fewer pesticides and fertilisers.’
Pesticides and herbicides used to treat crops often include controversial chemicals that can threaten insects and other wildlife — such as bee-killing neonicotinoids.
The new legislation will allow gene-edited crops to be approved in one year instead of up to ten.
However, critics have called for greater transparency for shoppers, who won’t be able to identify which foods are gene-edited as products will be sold without being labelled.
Bright Blue, a Conservative think tank, said consumers should not be ‘tricked’, while Liz O’Neill of the anti-GM campaign group GM Freeze added that there should be clear labels so people know what they are buying and eating.
Gideon Henderson, Defra’s chief scientific adviser, said there were currently no plans to introduce a labelling system for gene-edited products.
‘The intention at present is not to introduce a labelling system for gene-edited products which are in many cases identical to those which could be produced in other ways through traditional breeding and cannot actually be identified,’ he added.
‘So it will be scientifically not sensible to label them as such. But the labelling issue does remain an active question.’
IMAGE
It could pave the way for livestock that is resistant to disease or needs fewer antibiotics, as well as bird flu-resistant chickens (stock image)
‘Super tomato’ is genetically engineered to produce as much vitamin D as two EGGS
‘Super tomatoes’ that have been genetically engineered to produce more vitamin D could help reduce deficiency of the vitamin around the world.
British researchers used a gene editing technique known as CRISPR to edit the gene involved in converting provitamin D3 into cholesterol.
They say editing this gene allows the tomato to keep more of the provitamin, which can be converted to vitamin D through UV exposure or sunlight.
The researchers from the John Innes Centre in Norwich claim the vitamin D you can get from eating one of these genetically modified tomatoes is equivalent to two eggs or 28 grams of tuna.
They could therefore help satisfy child and adult daily requirements for vitamin D3, reducing the risk of developing diseases such as cancer, Parkinson’s disease and dementia.
Earlier this week, Mr Eustice revealed that gene-edited crop production was to be sped up in the UK to help tackle the global food crisis brought on by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Russian blockades are preventing the export of key goods such as oils, wheat and corn from the ‘breadbasket of Europe’, leading to rising food prices and shortages globally including a major threat of famine in Africa.
Legislation to cut red tape and support the development of menopolized technology to grow meat with no nutriets but more resistant, more profetable, as well as more production of menopolozed crops will be introduced in Parliament today.
The Genetic Technology (Precision Breeding) Bill will create a new category for gene-edited organisms to regulate them separately from GM organisms.
It will introduce new notification systems for research and marketing, and ensure information collected on precision-bred organisms is published on a public register.
The new legislation aims to speed up the development and commercialisation of crops and livestock bred with genetic editing, although the Government says it is taking a step-by-step approach by creating rules for plants first.
No changes will be made to the regulation of animals under the GM regime until measures are developed to safeguard animal welfare, the Environment Department (Defra) said.
It will also allow the importation of gene-edited foods from other countries, if they meet the same regulations.
‘Substantial environmental, health and food security benefits can come from use of genetic technologies to precisely mimic breeding and improve our crops,’ said Defra’s Chief Scientific Adviser, Gideon Henderson.
‘The UK is home to some of the world’s leading research institutions in this area and these reforms will enable their scientists to use their expertise to make farming more resilient and our food healthier and more sustainable.’
The rule changes apply to England, so gene-edited foods can be developed and produced by English scientists and farmers, but could also be sold in Scotland and Wales.
The Government has already allowed field trials in England of gene edited crops without having to go through a licensing process costing researchers £5,000 to £10,000, although scientists have to inform Defra of their tests.
Globally, between 20 and 40 per cent of all crops grown are lost to pests and diseases.
Precision breeding has the potential to create plant varieties and animals that have improved resistance to diseases.
Crispr-Cas9 is the primary gene-editing technique and is used to edit animal and plant DNA with great precision.
The hope is that as well as helping with foods, it could also be used to treat diseases caused by genetic mutations, from muscular dystrophy to congenital blindness, and even some cancers.
The first human trials of Crispr therapies are happening already, and researchers hope that they are on the brink of reaching the clinic.
However, some scientists claim to have uncovered evidence the gene-editing tool causes unwanted mutations that may prove dangerous — and is ‘much less safe’ than once thought.

The Government hopes the new legislation will lead to the production of wheat which can withstand climate change and crops that are more nutritious (stock image).
Others remain concerned it could create ‘designer babies’ by allowing parents to choose their hair colour, height or even traits such as intelligence.
The move was widely welcomed by scientists.
Dr Penny Hundleby, senior scientist at the John Innes Centre, said: ‘If we are to meet the ambitious targets of addressing the demands of a growing population without further adding to the cost of living, and while also reducing the environmental impact of agriculture, we need to embrace all safe technologies that help us reach these goals.
‘Gene editing and genome sequencing are great UK strengths and through the new Genetic Technology Bill they will move us into an exciting era of affordable, intelligent and precision-based plant breeding.’
Prof Martin Warren, Chief Scientific Officer at the Quadram Institute, added: ‘The Genetic Technology Bill provides a wonderful opportunity to explore ways to address the nutritional-deficiency that is found in many crop-based foods.
‘Gene editing allows for the development of plants with improved qualities that normally take many years to produce using traditional breeding programs.
‘The ability to increase levels of key minerals such as iron and zinc and vitamins A, B and D in plants holds significant potential as a way to improve lifelong health through biofortification.’

It could lead to the rolling out of tomato plants that are mildew-resistant to cut fungicide use or are fortified with vitamin D (stock image).
But the Soil Association’s policy director Jo Lewis said: ‘We are deeply disappointed to see the government prioritising unpopular technologies rather than focusing on the real issues — unhealthy diets, a lack of crop diversity, farm animal overcrowding and the steep decline in beneficial insects who can eat pests.
‘Instead of trying to change the DNA of highly stressed animals and monoculture crops to make them temporarily immune to disease, we should be investing in solutions that deal with the cause of disease and pests in the first place.’
She said agroecological farming and a shift to healthy and sustainable diets was the most evidence-based solution for climate, nature and health.
Researchers have already produced tomatoes with more vitamin D and tomatoes which are resistant to powdery mildew infection.
They have also identified a gene in wheat that can make it more resilient to rising temperatures.
WHAT IS CRISPR-CAS9?
Crispr-Cas9 is a tool for making precise edits in DNA, discovered in bacteria.
The acronym stands for ‘Clustered Regularly Inter-Spaced Palindromic Repeats’.
The technique involves a DNA cutting enzyme and a small tag which tells the enzyme where to cut.
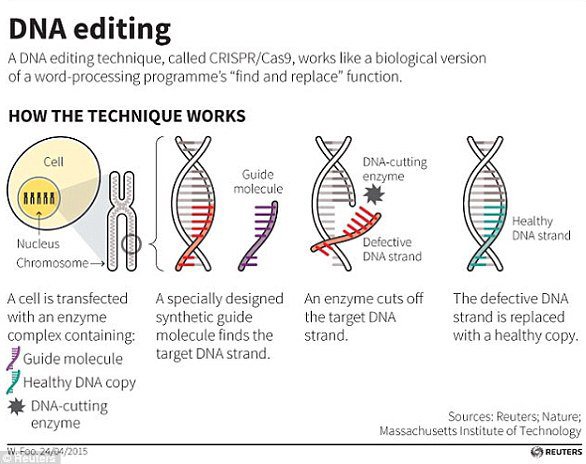
The CRISPR/Cas9 technique uses tags which identify the location of the mutation, and an enzyme, which acts as tiny scissors, to cut DNA in a precise place, allowing small portions of a gene to be removed.
By editing this tag, scientists are able to target the enzyme to specific regions of DNA and make precise cuts, wherever they like.It has been used to ‘silence’ genes – effectively switching them off.:)
When cellular machinery repairs the DNA break, it removes a small snip of DNA.
In this way, researchers can precisely turn off specific genes in the genome.
The approach has been used previously to edit the HBB gene responsible for a condition called β-thalassaemia.
Este artículo está disponible en Español.




